Carrier WiFi Offload
XNET Hotspot 2.0 and Wi-Fi Carrier Offload#
An introduction guide to Hotspot 2.0
May 6, 2024
Introduction#
1. Introduction
This document provides an overview of Hotspot 2.0 and Carrier Offload technologies, explaining their benefits for XNET and how XNET can leverage these technologies to improve connectivity and network management.
2. What is Hotspot 2.0?
Hotspot 2.0, also known as Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint or Passpoint 2.0, is an industry-standard technology that automates the process of finding and connecting to Wi-Fi networks. This technology enables devices to seamlessly connect to Wi-Fi hotspots without user intervention, using a set of predefined credentials. It enhances security and improves the user experience by utilizing enterprise-grade WPA2/WPA3 security protocols.
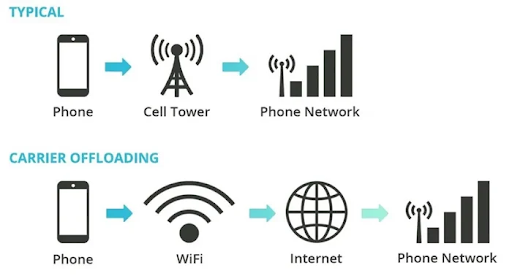
3. What is Carrier Offload?
Carrier Offload, often referred to in the context of mobile networks, is a technique used by cellular carriers to alleviate network congestion by offloading data traffic to Wi-Fi networks. This not only helps manage the data load on cellular networks but also provides users with faster and more reliable internet access.
Benefits of Carrier Offload#
4.1 Improved Network Efficiency
By implementing Hotspot 2.0, XNET can enhance the efficiency of its network. Devices can automatically connect to the best available Wi-Fi network, reducing the load on cellular networks and improving overall data throughput.
4.2 Enhanced User Experience
The seamless connection process offered by Hotspot 2.0 eliminates the need for manual network selection and password entry, improving the user experience. This is particularly beneficial in environments with high mobility, such as airports or shopping malls.
4.3 Cost-Effective Network Expansion
Carrier Offload allows XNET to handle increased data traffic without significant investments in additional cellular infrastructure. By utilizing existing Wi-Fi hotspots, XNET can expand network coverage and capacity in a cost-effective manner.
5. How XNET Benefits Carriers Using Wi-Fi
XNET's implementation of Hotspot 2.0 and Carrier Offload provides substantial benefits to carriers:
- Reduced Network Congestion: Offloading traffic to Wi-Fi reduces the load on cellular networks, especially in densely populated areas.
- Improved Service Quality: Carriers can offer higher data speeds and better connectivity, enhancing the overall quality of service.
- Cost Savings: Leveraging Wi-Fi for data traffic reduces the need for extensive cellular infrastructure upgrades.
Technical Overview#
6.1 Hotspot 2.0 Implementation
Hotspot 2.0 works by utilizing standards such as IEEE 802.11u for network discovery and selection, allowing devices to automatically discover network information and connect securely without user intervention. The technology utilizes standard protocols like EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) for authentication, ensuring security across network connections.
6.2 Carrier Offload Mechanisms
Carrier Offload involves dynamically switching from cellular to Wi-Fi networks when a Wi-Fi network is available and meets the quality of service requirements. This process is supported by protocols that manage the credentials and security automatically, ensuring a seamless user experience.
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+ +----------+
| Visited | | Wi-Fi | | Wi-Fi | | Cellular |
| Wi-Fi | | Hub | | Hub | | Provider |
| Network |<------>| Provider |<------>| Provider |<------>| Network |
| | RADIUS | | RADIUS | | RADIUS | |
| NAS | | RADIUS | | RADIUS | | RADIUS |
| |<------>| proxy |<------>| proxy |<------>| Server |
|Passpoint | IPSec +----------+ IPSec +----------+ IPSec +----------+
|PLMNID(s) |
Conventional Carrier Wi-Fi
+------------+
/|\
|
\|/
+------------+
|Passpoint |
| device |
| with |
| PLMNID |
| profile |
+------------+
OpenRoaming
+------------+ +---+ +------------+
| Visited |<----->|DNS|<-------------------> | Identity |
| Wi-Fi | +---+ | Provider |
| Network | DNS based peer | Network |
| NAS | discovery Configure | RADIUS |
| Passpoint |<---------------------- NAPTR, | Server |
| RCOI(s) | RadSec/TLS SRV and A | |
| | secured using Records | |
| | mTLS and WBA PKI | |
+------------+ +------------+
/|\
|
\|/
+------------+
|Passpoint |
| device |
| with |
| RCOI(s) |
| profile |
+------------+
- Conclusion
By embracing Hotspot 2.0 and Carrier Offload, XNET can enhance its network capabilities, offer a superior user experience, and achieve more efficient use of network resources. These technologies not only support current network demands but also prepare XNET for future growth and challenges in the telecommunications industry.
References
- APNIC 56. "OpenRoaming." September 2023.
- IETF. "Captive Portal API." RFC 8908. September 2020.
- IETF. "Captive-Portal Identification Using DHCP or Router Advertisements (RAs)." RFC 7710. December 2015.
- IETF. "CAPPORT Architecture." RFC 8910. September 2020.
- IETF. "Common Policy: A Document Format for Expressing Privacy Preferences." RFC 5580. August 2009.
- IETF. "Extensible Authentication Protocol Method for 3rd Generation Authentication and Key Agreement (EAP-AKA)." RFC 4187. January 2006.
- IETF. "IP Security (IPsec) and Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Document Roadmap." RFC 6071. February 2011.
- IETF. "Identity-Enabled Networks (IENs): A Non-Cryptographic Proposal for Additional Network Security." RFC 7585. May 2015.
- IETF. "OpenRoaming: Seamless Wi-Fi Roaming for the World." Draft document.
- IETF. "Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS)." RFC 2865. June 2000.
- IETF. "Transport Layer Security (TLS) Encryption for RADIUS." RFC 6614. May 2012.
- Intel Corporation. "Wi-Fi 7 and Beyond." PDF file, 2024.
- SimeonOnSecurity. "Ultimate XNET Connectivity Guide." Accessed May 7, 2024.
- SimeonOnSecurity. "Unlock Seamless Connectivity with Hotspot 2.0." Accessed May 7, 2024.